Generality about Physics
The aim of physics is to understand how the universe works.
Stephen Hawking
Physics is the study of the fundamental principles governing the natural world. It is a branch of science that seeks to explain the physical world around us. Physics is a quantitative science, which means that it relies on the measurement of physical quantities to describe the behavior of matter and energy. In physics, these quantities are often represented by mathematical equations.
The goal of physics is to understand how the universe works. Physicists seek to uncover the underlying principles that govern the behavior of matter and energy.
In doing so, they hope to gain a deeper understanding of the nature of the universe and the laws that govern it. Physics is a broad field of study that can be divided into five main branches: classical mechanics, electricity and magnetism, thermodynamics, optics, and modern physics. Each branch of physics has its own laws and principles governing the behavior of matter and energy.
Main branches of Physics
Classical Mechanics
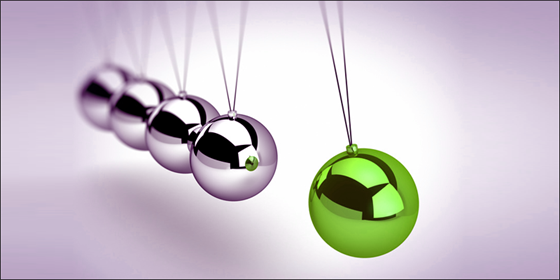
In classical mechanics, objects obey Newton’s laws of motion. These laws describe the behavior of objects in terms of their mass, velocity, and acceleration. The first law states that an object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless acted on by an external force. The second law states that the acceleration of an object is proportional to the force acting on it and is in the direction of the force. The third law states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Classical mechanics can be used to predict the motion of objects under the influence of forces. For example, if you know the mass of an object and the force acting on it, you can calculate the object’s acceleration. You can then use this information to predict the object’s position and velocity at any time in the future.
Classical mechanics is a powerful tool for understanding the world around us. It can be used to explain the motion of everything from falling apples to orbiting planets.
Electricity and Magnetism
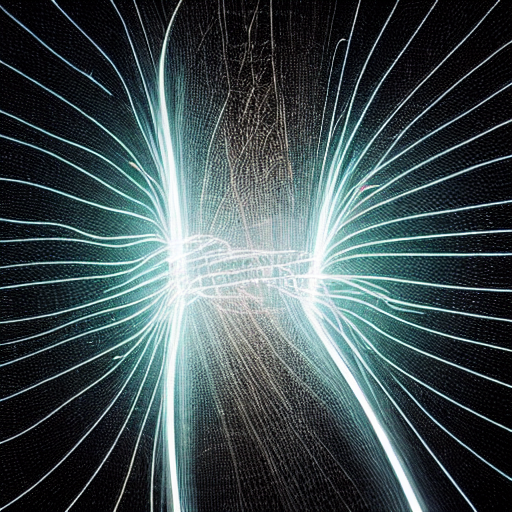
Electricity and magnetism are two forces that are often studied together. They are both related to moving electrons.
Electricity is the force that moves electrons through wires to create a current. Magnetism is the force that moving electrons create around a wire. The two forces are related because a moving electron creates both a magnetic field and an electric field.
Electricity is used to power our homes and appliances. Magnetism is used in many ways including in generators to create electricity, in motors to power machines, and in speakers to create sound.
Thermodynamics
In thermodynamics, heat is energy in transfer from one system to another or to its surroundings
Kondepudi, Prigogine
In thermodynamics, the branch of physics that deals with the energy and work of a system, the first law of thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. The second law of thermodynamics says that energy always flows from hot objects to cold objects.
In other words, thermodynamics is the study of how heat energy is converted into work energy. The first law of thermodynamics is sometimes called the law of energy conservation. The second law of thermodynamics is sometimes called the law of entropy.
Optics
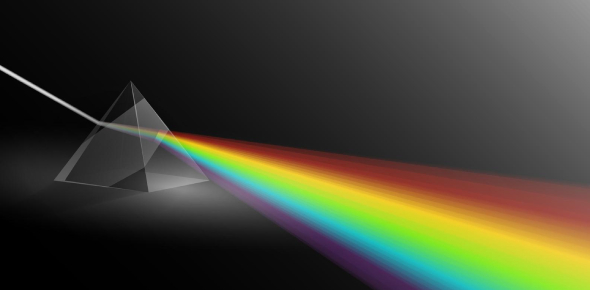
In optics, the study of light, there are many ways to bend and reflect light. Mirrors reflect light in a line perpendicular to the surface of the mirror. This is why we can see our reflection in a mirror.
There are other ways to bend light. A lens is a piece of glass that can bend light. Lenses are used in glasses, cameras, and microscopes. A concave lens bends light inward. A convex lens bends light outward.
We can see because light from objects enters our eyes and is bent by the lens in our eye. The light is then sent to our brains, where we see the objects.
Modern Physics
Modern physics is an attempt to come to grips with the fundamental nature of the universe.
Richard Feynman
Modern physics is the branch of physics that deals with the most up-to-date knowledge of the physical world. It is based on the two main theories of physics: quantum mechanics and relativity.
Quantum mechanics is the branch of physics that studies the behavior of matter and energy at the atomic and subatomic levels. It is the foundation of modern physics.
Relativity is the branch of physics that studies the behavior of matter and energy at high speeds. It is the foundation of modern physics.
All these branches will be discussed in more detail later.

One response to “What is Physics?”
[…] Chemistry vs Physics […]